A properly designed septic system is crucial for managing wastewater efficiently, especially in rural areas of Ontario where municipal sewer systems are unavailable. Understanding septic design in Ontario ensures compliance with regulations, prevents environmental contamination, and extends the system’s lifespan. Whether you’re a homeowner planning a new build or a contractor working on a septic project, knowing the legal requirements and best practices can save time and money. This guide covers everything you need to know about septic system design in Ontario, from regulations to installation and maintenance.
[toc]
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the Ontario Building Code is essential for septic system compliance. and,
- Site evaluation, soil testing, and system sizing are critical in the design phase. also,
- Hiring a licensed engineer ensures proper planning and approval. as well as,
- Routine maintenance, including inspections and pumping, prevents system failure. and,
- Alternative septic solutions, such as mound systems and advanced treatment units, may be necessary based on soil conditions.
Understanding Septic Design in Ontario
What is a Septic System?
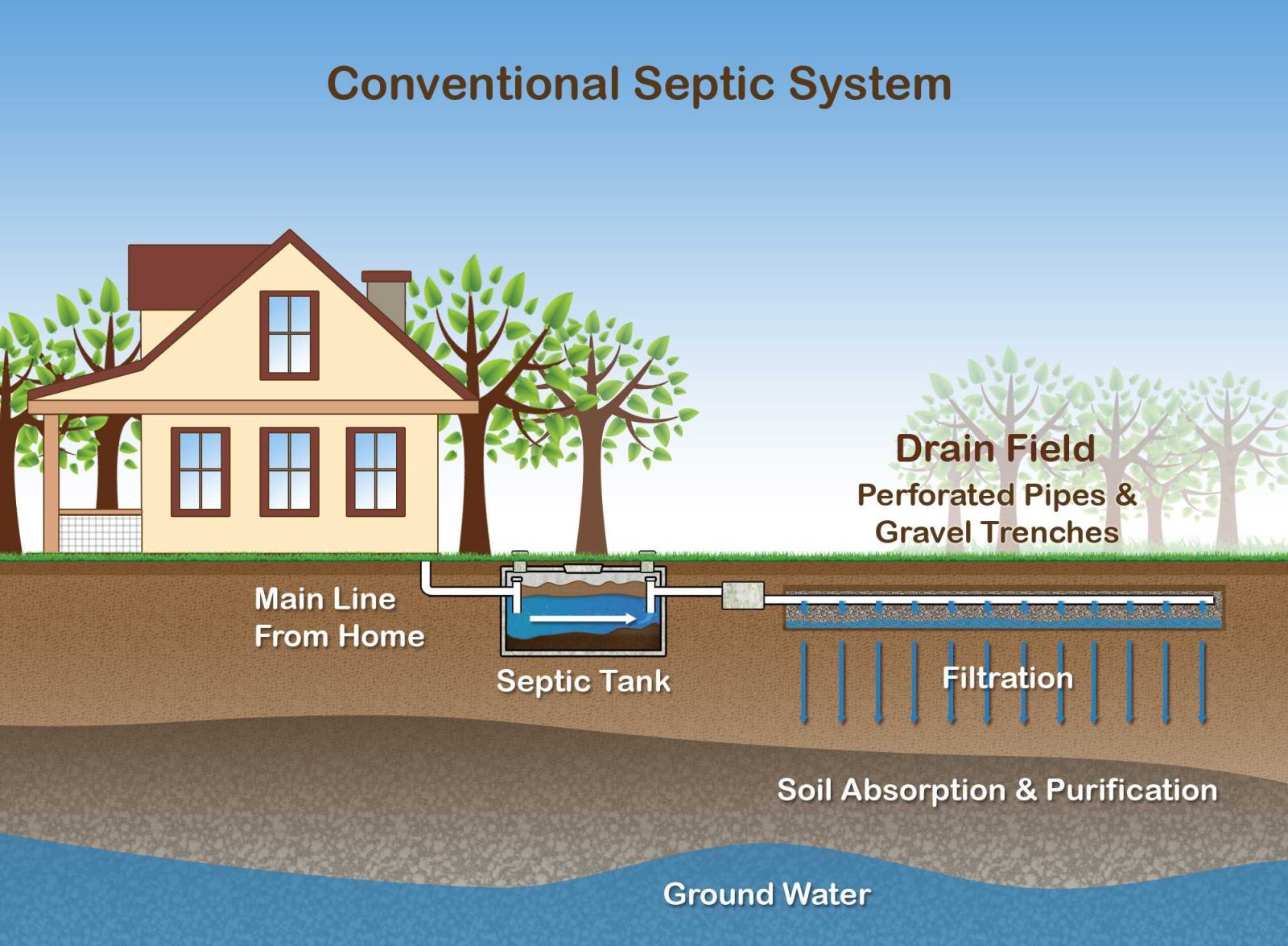
To clarify, a septic system is an on-site wastewater treatment solution that safely processes and disposes of household sewage. It is commonly used in rural and remote areas where municipal sewer services are unavailable. In Ontario, proper septic system design is essential for ensuring public health, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance.
Components of a Conventional Septic System
A typical septic system in Ontario consists of two primary components:
- Septic Tank
- Collects and separates wastewater into solid sludge, liquid effluent, and floating scum. and,
- Allows anaerobic bacteria to break down organic matter. also,
- Requires periodic pumping to prevent overflows.
- Leaching Bed (Drain Field)
- Distributes liquid effluent into the soil for natural filtration. moreover,
- Requires adequate soil permeability to avoid contamination. also,
- Designed based on percolation test results and site conditions.
How Septic Systems Work
Septic systems operate by treating wastewater naturally through a multi-step filtration process:
- Waste enters the septic tank, where solids settle at the bottom, and lighter materials float to the top. also,
- Effluent exits the tank and flows into the leaching bed. and,
- Soil absorption filters harmful bacteria and nutrients before returning water to the environment.
A well-designed septic system ensures long-term efficiency, environmental safety, and compliance with Ontario’s regulations.
Regulations Governing Septic Design in Ontario
Ontario Building Code (Part 8) Overview
Septic systems in Ontario are regulated under Part 8 of the Ontario Building Code (OBC). These rules govern:
- System design requirements based on property size and usage. and,
- Installation standards for tanks, pipes, and leaching beds. moreover,
- Inspection and maintenance obligations for property owners.
Failing to meet OBC standards can result in permit rejections, fines, or system failures.
Permit Requirements for Septic Installation
Before installing a septic system in Ontario, property owners must obtain a permit from their local municipality. The process typically involves:
- Site Evaluation – Conducting soil percolation tests to determine absorption rates. Furthermore,
- Design Submission – Providing detailed system plans prepared by a licensed engineer. and,
- Approval and Inspection – Undergoing on-site inspections to verify compliance.
Hiring a certified septic designer ensures all permit requirements are met.
Why Professional Design and Installation Matters
A licensed engineer or certified septic installer ensures:
- Proper system sizing based on daily sewage flow calculations. as well as,
- Compliance with municipal and provincial codes. also,
- Prevention of costly design flaws and environmental risks.
For expert design services, Elmid Design Inc., a professional engineering firm authorized by PEO (Professional Engineers Ontario), specializes in septic system planning and permitting in Ontario.
Design Considerations for Septic Systems in Ontario
Site Evaluation and Soil Testing
Before designing a septic system, a site evaluation is required to assess:
- Soil Permeability – Determines how well the soil absorbs wastewater. furthermore,
- Groundwater Levels – Ensures the leaching bed won’t contaminate water sources. as well as,
- Lot Size and Topography – Impacts system placement and drainage efficiency.
A percolation test (perc test) measures the rate at which soil absorbs water, a key factor in septic system design approval.
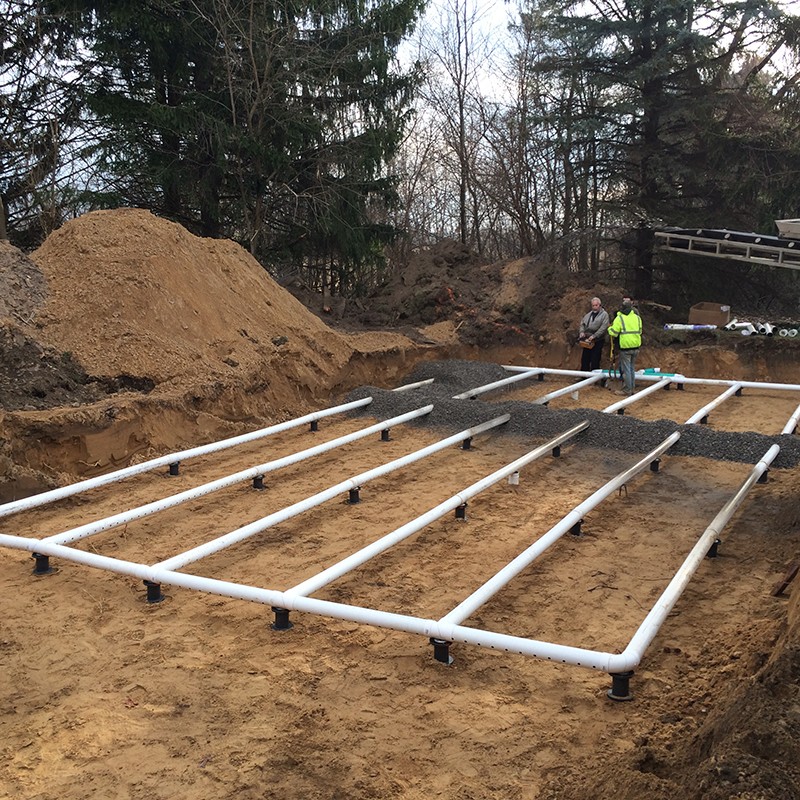

System Sizing and Capacity Planning
The size of a septic system depends on daily wastewater flow, typically calculated based on:
| Number of Bedrooms | Estimated Daily Flow (Litres/Day) | Recommended Tank Size (Litres) |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 Bedrooms | 1,600 L/day | 3,600 L |
| 3-4 Bedrooms | 2,400 L/day | 4,500 L |
| 5+ Bedrooms | 3,600 L/day | 6,000 L |
A properly sized system prevents overflow, clogging, and premature failure.
Alternative Septic System Options
If traditional septic systems are unsuitable due to soil conditions or space limitations, alternative options include:
- Mound Systems – Elevates the leaching bed for improved drainage. and,
- Aerobic Treatment Units (ATUs) – Uses oxygen to accelerate waste breakdown. also,
- Peat-Based Systems – Natural filtration using peat moss for enhanced treatment.
Alternative systems require specialized design and approvals but offer better performance in challenging environments.
Septic System Installation Process in Ontario
Planning and Design
Proper septic design planning involves:
- Creating detailed system layouts based on site evaluations. furthermore,
- Ensuring compliance with Ontario Building Code requirements. likewise,
- Coordinating with local authorities for approvals.
Construction Phases
The installation process follows several key steps:
- Excavation – Preparing the land for tank and drain field placement. and,
- Septic Tank Installation – Placing and connecting the tank to the house. furthermore,
- Leaching Bed Construction – Laying pipes and gravel for wastewater absorption.
Inspection and Final Approval
A final municipal inspection ensures:
- The system is installed correctly per design specifications. and,
- The leaching bed functions efficiently. also,
- All permit conditions are met.
Once approved, the system can be officially used for wastewater treatment.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Septic system design in Ontario requires careful planning, regulatory compliance, and professional expertise. Whether you’re installing a new system or upgrading an existing one, understanding the process ensures long-term efficiency and environmental safety.
If you need a licensed septic designer in Ontario, contact Elmid Design Inc. for expert planning, permit assistance, and system design. Proper septic design today prevents costly repairs and environmental hazards in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Septic Design in Ontario
How often should I have my septic system inspected?
Septic systems should be inspected at least once every 3-5 years by a licensed professional. However, if your household has high water usage or an older system, more frequent inspections may be necessary. Regular inspections help identify potential issues early and prevent costly repairs.
What are the costs associated with installing a septic system in Ontario?
The cost of installing a septic system in Ontario depends on factors like site conditions, system size, and design complexity. On average:
| Septic System Type | Estimated Cost Range (CAD) |
|---|---|
| Conventional System | $8,000 – $20,000 |
| Mound System | $15,000 – $30,000 |
| Advanced Treatment Unit | $20,000 – $40,000+ |
Additional costs may include permit fees, soil testing, and engineering services.
Can I install a septic system myself in Ontario?
No, septic system installation requires a permit and must comply with Ontario Building Code regulations. A qualified septic designer and a licensed installer must handle the design, installation, and inspection to ensure the system meets safety and environmental standards.
What permits are required for septic system installation in Ontario?
Before installation, you must obtain a septic system permit from your local municipality. The permitting process includes:
- Soil evaluation and percolation test to determine absorption capacity. and,
- Septic design plan submission by a licensed engineer. furthermore,
- Municipal review and approval before installation begins. also,
- Final inspection to confirm compliance before the system is operational.
How do I find a qualified septic system designer or installer in Ontario?
To find a licensed septic designer or installer, look for:
- Professional Engineers Ontario (PEO) certified firms like Elmid Design Inc. and,
- Ontario Onsite Wastewater Association (OOWA) registered professionals. as well as,
- Local health departments and municipal offices that provide licensed contractor lists. additionally,
Hiring a qualified expert ensures code compliance, efficiency, and long-term system performance

Septic System Maintenance and Troubleshooting in Ontario
A well-maintained septic system ensures long-term efficiency, prevents environmental contamination, and saves thousands in repair costs. Homeowners in Ontario must follow proper septic maintenance guidelines to comply with regulations and extend the lifespan of their system. Ignoring maintenance can lead to costly failures, property damage, and groundwater pollution. This guide covers everything you need to know about septic system maintenance, common problems, and troubleshooting solutions.
[toc]
Key Takeaways
- Regular inspections and pumping prevent system failure and costly repairs. and,
- Proper waste disposal protects septic system function and efficiency. additionally,
- Common warning signs like slow drainage and bad odors indicate potential problems. also,
- Routine maintenance extends the lifespan of your system and protects groundwater. as well as,
- Professional servicing is essential for complex issues and regulatory compliance.
Maintaining Your Septic System in Ontario
Routine Inspections: How Often Should You Check Your Septic System?
Regular inspections help detect potential issues early, preventing costly breakdowns. In Ontario, homeowners should:
- Schedule a professional inspection every 3-5 years. and,
- Monitor water levels and sludge accumulation in the septic tank. also,
- Check for drain field saturation and pooling water.
Licensed professionals can assess whether your system requires pumping, repairs, or upgrades.
Septic Tank Pumping Schedule
Septic tanks accumulate solid waste over time. Without proper pumping, solids can clog the system, leading to backups or failure. Pumping frequency depends on:
| Household Size | Septic Tank Size (Litres) | Recommended Pumping Interval |
|---|---|---|
| 1-2 people | 3,600 L | Every 4-5 years |
| 3-4 people | 4,500 L | Every 3-4 years |
| 5+ people | 6,000 L | Every 2-3 years |
Failure to pump your septic tank on time can lead to overflow, system failure, and costly repairs.
Best Practices for Septic System Care
To keep your septic system functioning properly, follow these essential maintenance tips:
- Limit Water Usage: Excessive water flow can overload the system. Use water-saving appliances and spread out laundry loads. additionally,
- Use Septic-Safe Products: Avoid harsh chemicals, antibacterial soaps, and bleach-based cleaners, which can kill beneficial bacteria in the tank. also,
- Proper Waste Disposal: Never flush non-biodegradable items like wipes, paper towels, or feminine hygiene products. and,
- Protect the Drain Field: Keep vehicles and heavy objects off the leaching bed to prevent soil compaction.
Following these practices prolongs your system’s lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Solutions
Signs Your Septic System is Failing
A failing septic system can cause major health and environmental risks. Watch for these warning signs:
- Slow Draining Sinks and Toilets – Indicates potential blockages or tank overflow. moreover,
- Gurgling Noises in Pipes – Suggests trapped gas or drainage problems. also,
- Foul Odors Around the Property – May signal a leaking septic tank or overloaded drain field. and,
- Pooling Water Near the Drain Field – Shows poor absorption and possible system failure. as well as,
- Lush, Green Grass Over the Drain Field – Can indicate wastewater surfacing instead of absorbing into the soil.
Causes of Septic System Failures
Several factors contribute to septic system problems, including:
- Lack of Pumping: When the tank overflows, solids clog the drain field. furthermore,
- Excessive Water Use: Overloading the system reduces treatment efficiency. and,
- Soil Compaction: Driving over the drain field prevents proper absorption. and,
- Tree Root Intrusion: Roots can penetrate pipes and block drainage. also,
- Improper System Design: A poorly sized septic system cannot handle household wastewater demands.
Addressing these common causes early prevents expensive repairs and environmental damage.
How to Fix Septic System Problems
If you notice septic system issues, take the following steps:
- Reduce Water Usage – Limit water flow until the problem is diagnosed. likewise,
- Check for Clogs – Inspect drains for obstructions. and,
- Schedule a Pumping Service – Remove excess waste if the tank is full. as well as,
- Inspect the Drain Field – Ensure the soil isn’t saturated or blocked. also,
- Contact a Professional – Licensed experts can assess and repair complex problems.
Hiring a licensed septic service provider in Ontario ensures the problem is fixed correctly and complies with local regulations.
How to Extend the Life of Your Septic System
A well-maintained septic system can last 25-40 years. Follow these preventative measures to maximize lifespan:
- Pump the Tank Regularly – Prevents solid waste buildup. in addition,
- Limit Harsh Chemicals – Protects beneficial bacteria for waste breakdown. also,
- Use a Bacteria Additive – Helps maintain a healthy microbial balance. and,
- Divert Rainwater Away from the Drain Field – Prevents oversaturation. as well as,
- Monitor Your System Annually – Early detection prevents costly repairs.
Taking preventative action today can save thousands in replacement costs.
When to Call a Septic Professional in Ontario
DIY vs. Professional Maintenance
While homeowners can follow basic maintenance practices, certain tasks require professional expertise:
| Task | DIY Possible? | Requires Professional? |
|---|---|---|
| Regular inspections | No | Yes |
| Pumping the tank | No | Yes |
| Checking for clogs | Yes | No |
| Repairing drain field | No | Yes |
| Installing a new system | No | Yes |
If you experience persistent septic problems, hire a licensed septic expert for an in-depth assessment and repairs.
Choosing a Licensed Septic System Expert in Ontario
When selecting a septic system designer, installer, or inspector, consider:
- Certification – Ensure they are licensed by Professional Engineers Ontario (PEO) or registered with the Ontario Onsite Wastewater Association (OOWA).
- Experience – Look for professionals with proven septic system expertise.
- Customer Reviews – Check online ratings and testimonials.
For reliable septic system design and installation services, Elmid Design Inc. offers expert solutions tailored to Ontario homeowners.
Final Thoughts: Protecting Your Septic System Investment
Proper septic system maintenance is crucial for efficiency, longevity, and environmental safety. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, homeowners in Ontario can prevent failures, save money, and comply with regulations.
If you need professional septic system design, maintenance, or repairs, contact Elmid Design Inc. for expert guidance and services. Protect your investment with proactive maintenance and professional care today.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Septic System Maintenance in Ontario
How do I know if my septic tank needs pumping?
Signs that your septic tank needs pumping include slow drainage, bad odors, pooling water around the drain field, and sewage backups in your home. To prevent issues, schedule a septic tank pumping every 3-5 years based on household size and water usage.
What should not go into a septic system?
Avoid flushing or draining the following into your septic system:
- Non-biodegradable items (wipes, paper towels, diapers).
- Fats, oils, and grease, which cause clogs.
- Harsh chemicals like bleach, pesticides, and drain cleaners.
- Excessive food waste or coffee grounds.
- Medications, which disrupt bacterial balance in the tank.
Can I use additives to improve my septic system’s performance?
While some biological additives may help maintain bacterial balance, they are not a substitute for proper maintenance. Many chemical additives can be harmful and cause system damage. The best way to maintain your septic system is through regular pumping, proper waste disposal, and water conservation.
What happens if my septic system fails?
A failing septic system can lead to property damage, health hazards, and environmental contamination. If you notice signs of failure, such as standing water, bad odors, or sewage backups, take immediate action by reducing water usage and calling a licensed septic professional for an inspection and repair.
Can I build or plant over my septic drain field?
No, you should keep the drain field clear of structures, heavy objects, and deep-rooted plants. The leaching bed needs oxygen and proper soil absorption to function correctly. Instead of deep-rooted plants, use grass or shallow-rooted vegetation to prevent soil erosion.
How can I extend the lifespan of my septic system?
To maximize the life of your septic system:
- Pump the tank regularly to prevent sludge buildup.
- Limit water usage to avoid overloading the system.
- Avoid harsh chemicals that kill beneficial bacteria.
- Keep the drain field clear of heavy objects and plant roots.
- Schedule regular inspections to catch issues early.
Who should I contact for professional septic system maintenance in Ontario?
For licensed septic system design, installation, and maintenance, contact Elmid Design Inc. Their team of PEO-certified engineers provides expert septic system solutions for homeowners and builders in Ontario.
Why Choose Elmid Design Inc. for Your Septic System Design in Ontario?
When it comes to septic system design and approval in Ontario, hiring a licensed and experienced engineering firm is essential. Elmid Design Inc. is a Professional Engineers Ontario (PEO)-certified company specializing in septic system planning, permitting, and regulatory compliance. With a deep understanding of Ontario Building Code (Part 8) and municipal requirements, our team provides customized septic solutions for residential, commercial, and industrial projects. From soil evaluations and percolation testing to engineered design plans and permit approvals, we ensure your system meets local and environmental standards. Whether you’re building a new home, upgrading an existing system, or dealing with a permit challenge, Elmid Design Inc. delivers expert guidance, cost-effective designs, and hassle-free approvals. Contact us today to ensure your septic system is efficient, compliant, and built to last.
Geographic Locations That We Service:
Our Licensed Professional Engineers specializing in Engineered Site Grading Plans offer the best-engineered site grading plan, lot grading and erosion plan, and drainage plan to obtain site plan approval and building permits in Ontario, including a wide range of municipalities. Each area boasts unique features and requirements, making our tailored approach essential for success.
Toronto and Surrounding Areas
In the vibrant heart of Ontario, we service Toronto (City of Toronto) and surrounding areas. Additionally, we cover Oshawa (City of Oshawa), Pickering (City of Pickering), and Clarington (Municipality of Clarington). Furthermore, our expertise extends to Ajax (Town of Ajax), Whitby (Town of Whitby), Brock (Township of Brock), Scugog (Township of Scugog), and Uxbridge (Township of Uxbridge).
Halton Region
Moving to the Halton Region, our services encompass Burlington (City of Burlington) and Halton Hills (Town of Halton Hills). Also included are Milton (Town of Milton) and Oakville (Town of Oakville).
Peel Region
In the Peel Region, we provide services in Brampton (City of Brampton), Mississauga (City of Mississauga), and Caledon (Town of Caledon).
York Region
Our services in the York Region cover Vaughan (City of Vaughan), Aurora (Town of Aurora), and East Gwillimbury (Town of East Gwillimbury). We also cater to Georgina (Town of Georgina), Markham (City of Markham), Newmarket (Town of Newmarket), Richmond Hill (City of Richmond Hill), Whitchurch-Stouffville (Town of Whitchurch-Stouffville), King (Township of King), and Bradford-West Gwillimbury (Town of Bradford-West Gwillimbury). Each municipality here offers a distinct setting, requiring our specialized approach.
Other Southern Ontario Cities and Towns
We also serve many other cities and towns in Southern Ontario. These include Hamilton (City of Hamilton), St. Catharines (City of St. Catharines), Niagara on the Lake (Town of Niagara on the Lake), Brant (County of Brant), Cambridge (City of Cambridge), Kitchener (City of Kitchener), Waterloo (City of Waterloo), and Woodstock (City of Woodstock). Furthermore, we operate in Guelph (City of Guelph), Centre Wellington (Township of Centre Wellington), Shelburne (Town of Shelburne), Orangeville (Town of Orangeville), New Tecumseth (Town of New Tecumseth), Essa (Town of Essa), Collingwood (Town of Collingwood), Wasaga Beach (Town of Wasaga Beach), Barrie (City of Barrie), Midland (Town of Midland), Orillia (City of Orillia), Ramara (Town of Ramara), Minden Hills (Town of Minden Hills), North Kawartha (Town of North Kawartha), Kawartha Lakes (City of Kawartha Lakes), Peterborough (City of Peterborough), Selwyn (Town of Selwyn), and Brighton (Municipality of Brighton).